Hi, my name is Allison Schaaf, my own fertility journey, including 5 miscarriages, inspired me to create this website to help YOU navigate your own fertility journey.
Here are my main takeaways I would share with you as a friend:
- Excess histamine may contribute to miscarriage, but is poorly understood and under recognized.
- This article takes an in-depth look at histamine intolerance and how it may impact fertility. It also looks at the research related to treatment options, including diet, supplements and medications that may help.
- Histamine intolerance can be tricky to diagnose so it’s important to find a doctor or health professional with experience specific to histamine intolerance to help determine if this is something that might be impacting your fertility.
Of course, I also recommend you do your own research! That is why I have coordinated these articles with the nitty-gritty details and links to research so you can best decide what works best for you, read on for more! And don’t miss my Action Steps at the bottom of the article!
Table of Contents
What is histamine intolerance?
Causes and contributing factors of histamine intolerance
Symptoms of histamine intolerance
Histamine Intolerance and Miscarriage
Diagnosis of histamine intolerance
Treatment for Histamine Intolerance
Histamine intolerance or diamine oxidase (DAO) deficiency is a poorly understood and poorly recognized condition that may cause miscarriage. There are many potential causes, such as the lack of histamine-degrading enzymes and digestive disorders. Histamine intolerance affects about 1% of the population, ~80% of which are middle-aged females 1. Some symptoms of histamine intolerance are similar to allergic diseases, such as hives and asthmatoid wheezing.
Some European countries recognize and treat histamine intolerance. In other countries, it is frequently overlooked and may not be recognized as a condition. However, there is some, although limited, research about histamine intolerance.
Diagnosing and addressing histamine intolerance, especially in the context of recurrent miscarriage, requires more than just an antihistamine drug. Our histamine series will cover everything you need to know about histamine intolerance based on the latest published research.
In Part 1: Histamine and Pregnancy, we covered the roles of histamine in general health, pregnancy, and miscarriage. In this article, Part 2, we will cover the definition, symptoms, causes, and potential treatments for histamine intolerance.
What is histamine intolerance?
Histamine intolerance is not an intolerance to histamine in your body. Rather, it is mainly a food intolerance resulting from increased histamine burden and reduced ability to breakdown histamine. People with histamine intolerance often develop symptoms due to excessive histamine after consuming foods high in biogenic amines or histamine liberators, which stimulate histamine release.
Although many symptoms of histamine intolerance resemble allergic diseases, it is a pseudo-allergic disease because it is not mediated by IgE. Allergies involve IgE recognizing allergens and causing histamine release, whereas histamine intolerance entails similar symptoms without IgE.
Foods that are high in histamine or biogenic amines include 2:
- Fermented foods, such as sauerkraut, kimchi, kombucha, pickles, natto, yogurt, kefir, vinegar, miso, soy sauce, sourdough bread
- Cheese, buttermilk, cultured butter
- Undistilled alcoholic beverages, such as beer and wine
- Cured foods, such as sausage, pepperoni, salami
- Smoked or slow-cooked meat
- Spinach
- Eggplant
- Tomatoes, including sauces
- Chocolate
- Paprika
- Pork
- Dry-aged meat
- Canned and processed food
- Avocados
- Some ripe fruits
- Meat, fish, and shellfish that are not fresh
- Leftovers
Histamine liberators or foods that stimulate histamine release include:
- All alcohol
- Tobacco
- Papaya
- Strawberries
- Pineapple
- Citrus
- Egg whites
- Nuts
- Peanuts
- Artificial food colors
Causes and contributing factors of histamine intolerance
Histamine intolerance is caused by low function of DAO due to low DAO activity or low DAO levels. It is a complex condition with multiple contributing causes, including:
Gut lining damage
The damage in the gut lining reduces DAO produced in the gut, thus reducing the ability to break down histamine from food. The gut mucosa can be damaged from food sensitivities, Celiac disease, small intestine bacterial overgrowth, inflammatory bowel disease, and other gut infections 3. Chemotherapy also damages the gut lining.
Trauma and chronic stress
Stress can cause inflammation of the gut barrier4. Also, stress hormones activate mast cells 5. Therefore, stress can trigger and worsen histamine intolerance.
Allergic or autoimmune tendency
The allergic or autoimmune tendency can contribute to elevated histamine, and vice versa 6.
Genetics
Single nucleotide polymorphisms within the DAO gene are linked to lower DAO activity levels 7. The HNMT enzyme, which requires SAMe, a product of methylation may also increase histamine levels 8.
While methylation may affect HNMT activity, there is no evidence that MTHFR variants cause histamine intolerance. In fact, some methylation supplements can trigger histamine release, causing symptoms in people with histamine intolerance.
Also, it is unclear whether methylation supplements may increase the risk of allergic diseases 9.
Gut microbiome
The combination of gut bacteria with more histamine-generating, as opposed to histamine-degrading bacteria, may worsen histamine intolerance. People with histamine intolerance have less Bifidobacteria 10. The following species of probiotics support histamine breakdown:
- Bifidobacterium longum 11
- Bifidobacterium bifidum 12
- Bifidobacterium infantis 13
- Lactobacillus salivarius 14
- Lactobacillus plantarum 15
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Lc705 16
The following species may increase histamine 17:
- Lactobacillus reuteri 18
- Lactobacillus caseii
- Lactobacillus bulgaricus
- Lactobacillus helveticus
- Lactobacillus delbrueckii
Clinically, however, Dr. Aumatma Shah, ND, of Holistic Fertility Center found spore-based probiotics more beneficial than these Bifidobacteria or Lactobacilli strains for histamine intolerance.
DAO-blocking agents or drugs
These can cause temporary histamine intolerance, including (but are not limited to):
- Cefuroxime
- Cefotiam
- Chloroquine
- Aminophylline
- Verapamil
- Alprenolol
- Dihydralazine
- Heparin
- Cimetidine
- Aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Symptoms of histamine intolerance
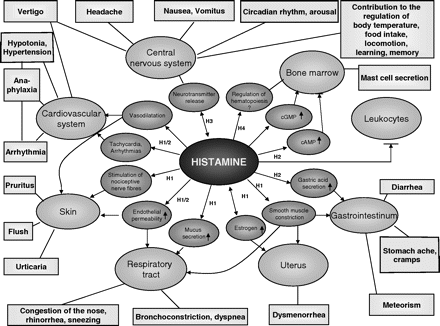
Symptoms of histamine intolerance are similar to allergies or other symptoms of excess histamine and can be unspecific, such as20:
- Diarrhea or diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome
- Headache
- Nasal congestion
- Asthma and wheezing
- Low blood pressure
- Abnormal heart rhythm
- Hives
- Itchy skin
- Flushing
- Painful period
- Cyclical headache or digestive symptoms
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Nausea and vomiting
- Joint pain or worsen chronic pain
- Brain fog
- Fatigue
- Anxiety, irritability, and moodiness
- Insomnia
- Inability to focus or attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder21
- Interstitial cystitis22
- Pregnancy complications and miscarriage
Many people with histamine intolerance suffer from some of these symptoms, while others remain symptom-free until they eat high histamine and histamine-liberating foods. A clear sign of histamine intolerance is if these symptoms worsen after consuming these foods, but are relieved or prevented by supplementing with the diamine oxidase enzyme 23.
Histamine Intolerance and Miscarriage
No study has conclusively confirmed that histamine intolerance causes miscarriage, although it makes sense that excess histamine and inflammation can disrupt a pregnancy. Also, there are many other reasons histamine could be elevated (See “Conditions Often Confused with Histamine Intolerance).
Low maternal DAO levels are associated with a 16.6 times increased risk of miscarriage at 12 weeks24. However, we still don’t know if the low DAO caused the miscarriages or if the miscarriage reduced the DAO.
The elevated histamine may throw off the estrogen and prostaglandin balances, contributing to to the miscarriage. The reduced DAO may also explain the allergic symptoms some women experience right before a miscarriage, although allergic symptoms can also happen during a healthy pregnancy.
If you have had miscarriage that you suspect could be due to excess histamine, work with the appropriate physician to get the right diagnosis and treatment. In Part 1: Histamine and Pregnancy, we also discussed other conditions that are often confused with histamine intolerance but need different treatments.
Diagnosis of histamine intolerance
Currently, there is no standard of care for diagnosing histamine intolerance. However, studies have suggested the following for patients with symptoms and history of histamine intolerance:
1) Blood diamine oxidase levels
Low nonpregnant serum DAO levels at <10 U/mL may indicate histamine intolerance25. However, this test is not common. In the US, the only lab that tests for DAO levels is Dunwoody Labs.
2) Skin prick-wheal test
The skin prick-wheal test is similar to an allergy skin test. After applying a 1% histamine solution with a needle, 79% of people with histamine intolerance still have an itchy bump for longer than 50 minutes 26.
3) Blood histamine levels
Elevated blood histamine levels shortly after consuming histamine-containing food may indicate histamine intolerance. However, histamine testing alone is unreliable as it is an unstable molecule. Blood histamine levels may increase with stress, time of day, and parts of the menstrual cycle 27.
Table: Normal ranges for blood histamine levels 2829.
| Healthy Total blood histamine | Plasma histamine | |
| Preconception | 50 – 60 ng/mL | 0.3 – 0.7 ng/mL |
| First trimester | 50 – 60 ng/mL | Not available |
| Second trimester | 9 – 48 ng/mL | Not available |
| Third trimester | 30 – 54.7 ng/mL | Not available |
4) Elimination-blind challenge
Many people who struggle with histamine intolerance may suffer from many obscure symptoms without knowing that they are related to food. A good standard for diagnosing histamine intolerance is to first minimize histamine from your diet in an elimination diet, then do a double-blind placebo-controlled challenge 30.
In this challenge, you will take a number of pills with and without histamine, without knowing which is which. If you predictably develop symptoms in response to the histamine pills and gain significant relief with DAO supplements, then you likely do have histamine intolerance.
Keep in mind that the challenge should be medically supervised. The challenge should be done in a medical office because of the potential for histamine to cause severe or life-threatening reactions. Also, work with a qualified dietician or nutritionist through the elimination and reintroduction phase to make sure the diagnosis is accurate.
Treatment for Histamine Intolerance
Addressing histamine intolerance as a food intolerance involves addressing the root causes and removing foods that trigger reactions. In some cases, antihistamines, mast cell blockers, and nutritional supplements may be helpful.
While we know that much of histamine intolerance relates to the gut, scientists still don’t fully understand how much placenta DAO levels reflect gut DAO levels. However, excessive histamine levels during pregnancy are bad for pregnancy outcomes. Therefore, managing high histamine with the following strategies may be beneficial if you have elevated histamine and repeat miscarriages. Ideally, if possible, it is better to stabilize your histamine symptoms before conception.
1) Testing and treating digestive problems
The lining of the small intestine is a major producer of DAO. Both overt digestive diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease, and subtle gut inflammation, such as small intestine bacterial overgrowth, can cause histamine intolerance. Some subtle gut inflammation may be caused by food-related inflammation, such as non-celiac gluten sensitivity, oxalate sensitivity, and lectin sensitivity 3132.
Conventional gastroenterologists can rule out or diagnose digestive conditions, whereas functional medicine physicians specialize in optimizing gut barrier function. If you have histamine intolerance without diagnosable digestive conditions, consider working with a functional medicine physician who specializes in histamine intolerance.
2) Identifying and managing DAO blockers
Alcohol, tobacco, and many medications may block DAO. However, most people can use these substances without triggering histamine intolerance. If you started to develop symptoms after introducing alcohol or tobacco, stop using them, especially during pregnancy. If your histamine symptoms started after starting on medications that may block DAO, speak to your prescribing physician about managing the DAO-blocking side effects.
3) Elimination diet and limiting dietary histamine
A diet to manage histamine intolerance can be very restrictive and should be medically supervised. It involves eliminating or limiting high-histamine foods. This includes ensuring all your food is fresh, and freeze instead of refrigerating your leftovers. Fortunately, you may be able to bring back some of the excluded foods if they do not provoke any symptoms.
Low-histamine foods include:
- Fresh meat and fish
- Fresh non-citrus fruits
- Gluten-free grains
- Coconut
- Fresh vegetables other than spinach and nightshades
- Cooking oils
If you do have a digestive condition that caused histamine intolerance, such as IBS, your diet restrictions should also take into account the digestive condition.
4) DAO supplements
Many people who struggle with histamine intolerance find relief taking DAO enzyme supplements 33. However, these supplements are expensive and do not treat the root causes.
5) Antihistamines
Antihistamine drugs bind to histamine receptors and prevent histamines from taking effects. These drugs are used to treat the symptoms and help manage histamine intolerance.
Benadryl is a histamine blocker that also increases diamine oxidase (DAO) production. It is better taken at night since it induces sleepiness. In fact, it is also sometimes used as an occasional sleep aid 3435. Benadryl may also decrease anxiety and increase serotonin in the brain, similar to SSRI antidepressants. In fact, many antidepressants and antipsychotics were developed based on Benadryl’s chemical structure 36.
Elevated histamine during pregnancy can contribute to hyperemesis gravidarum (HG, severe morning sickness). Some medications to treat HG are also antihistamines that have been shown to be safe during pregnancy.
Diclegis and Bonjesta (doxylamine succinate combined with vitamin B6) block histamine H1 receptors in the brain, effectively blocking the vomit nerve conduction 37. Vitamin B6 supports DAO production and activity 38. Unisom is an allergy medication that contains doxylamine succinate without vitamin B6.
Does blocking histamine cause or prevent pregnancy complications? – Interestingly, a 1997 aggregate analysis of 200,000 women who used antihistamines during their first trimester found that the antihistamines may reduce the risk of fetal malformation by about 24% 39. However, another aggregate study published in 2017 found no effect 40. Typically, excessive nausea and vomiting can contribute to nutrient deficiencies and thus worse outcomes, so these antihistamines may help by improving these women’s wellbeing rather than directly preventing miscarriage.
6) Mast cell stabilizer
Mast cell blocking drugs and natural substances may be prescribed to control symptoms of histamine intolerance and mast cell activation disorder.
Cromolyn sodium is a drug for asthma and respiratory conditions that have been used nasally in pregnant women 41.
Quercetin🅧 is a substance in green tea and onions that stabilize mast cells. However, quercetin is poorly absorbed, and it is unclear whether it is safe for pregnancy at pharmaceutical doses 42. Several other flavonoids may also stabilize mast cells, although with limited absorption and evidence of safety in pregnancy43.
7) Nutrients and supplements that may help with histamine intolerance
Certain nutrients support DAO levels and function. However, while these nutrients are safe, we have very limited evidence to support their effectiveness in treating histamine intolerance.
Nutrient density – A small Japanese study involving 34 women examined the dietary intake of calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, polyunsaturated fatty acids, zinc, iron, and vitamin B12 relative to energy intake. They found that these nutrients correlated with higher DAO during the luteal phase 44. High DAO is a sign of better gut barrier function and improved ability to break down histamine.
Dietary fat – a high-fat meal may increase DAO production in the gut lining 45
Vitamin C, B6, and copper support DAO function and also have natural antihistamine effects 4647.
Takeaway
- Histamine intolerance is a real condition that is not well-recognized in the medical field.
- If you suspect you may have histamine intolerance, work with a professional to get diagnosed and treated, don’t guess or try to do it yourself.
- You may need to work with a medical doctor, a functional medicine doctor, and a nutritionist to prepare your body for pregnancy if you have histamine intolerance and repeat miscarriage.
- Histamine intolerance is obscure and can be easily confused with many conditions, so it is important to understand what you have before treating it. In Part 1: Histamine and Pregnancy, we discuss these other similar conditions.
Next Steps to Consider
- If you suspect you may have histamine intolerance, it is important to find a doctor or health care professional that specializes in histamine intolerance to help with a diagnosis.
- Consider an elimination diet to help in diagnosing a histamine intolerance. I recommend finding a dietitian or other health professional that can help you with this process as they are tricky to do on your own.
- If you do have a histamine intolerance, work with your doctor using the above diet, lifestyle, supplement & other treatment options to find a solution that works best for you.
References




0 Comments