Hi, my name is Allison Schaaf, my own fertility journey, including 5 miscarriages, inspired me to create this website to help you navigate your own fertility journey.
Here are the key takeaways I would share with you as a friend:
- Testing for DNA fragmentation is not part of a standard sperm analysis and in my experience, many doctors do not routinely test for this
- Encouragingly, there is research on ways to prevent DNA fragmentation that might ultimately lead to a healthy pregnancy
I also recommend you do your own research and speak to your doctor. That is why I have coordinated these articles with the nitty-gritty details and links to research so you can make an informed decision on what works best for you… read on for more! And don’t miss my Next Steps section at the bottom.
Table of Contents
What is sperm DNA fragmentation?
Different types of sperm DNA damage
What causes sperm DNA fragmentation?
What are sperm DNA fragmentation symptoms?
Sperm DNA fragmentation diagnosis
Treatments for Sperm DNA fragmentation
Can you have a successful pregnancy with sDF?
Sperm DNA fragmentation (sDF) may be a male factor contributing to recurrent miscarriages and over 50% of infertility cases. 1 Common semen analysis may miss sperm DNA fragmentation, so if you want to know specifically about your DNA damage, a direct sDF test is needed. However, most doctors disagree on whether testing and treating sDF is helpful because the evidence so far has been mixed. 2 A 2019 meta-analysis demonstrated a clear association between sperm DNA damage and recurrent pregnancy losses. 3 In this article, we will cover sperm DNA fragmentation causes, lab tests, and treatments.
What is sperm DNA fragmentation?
Because sperms need to be compact and agile, most cellular components, including its own DNA repair apparatus, are eliminated. When a sperm leaves its production factory, it naturally sustains some DNA damage. Fortunately, once fertilized, the egg can repair some of the damage before developing into an embryo. 4 Sperm DNA fragmentation is a problem when the sperm DNA is so damaged that the egg’s natural DNA repair machinery cannot sufficiently repair it.
Since the DNA contains genes necessary for healthy fetal development and life sustenance, excessive DNA damage can lead to miscarriage, congenital disorders, and childhood cancers. 56 Miscarriages due to sDF tend to occur early, either chemical or within the first 13 weeks.
Different types of sperm DNA damage
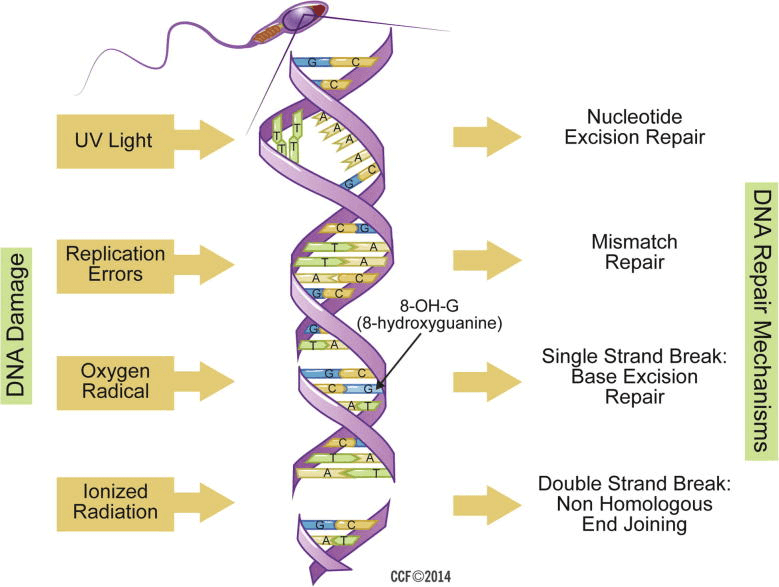
A DNA molecule is present in two strands forming a double helix. When one of the strands breaks, the DNA damage is called a “single strand break” or a nick. Whereas, when both strands break, the DNA damage is called “double strand break.” Other types of DNA damage may include skipping a base pair (basic unit of a DNA polymer) or incorporating an incorrect base pair into the genome.
The strand breaks are more likely to destabilize the genome, causing infertility and miscarriages. Notably, double-stranded breaks are harder to repair and more likely to disrupt embryonic development.
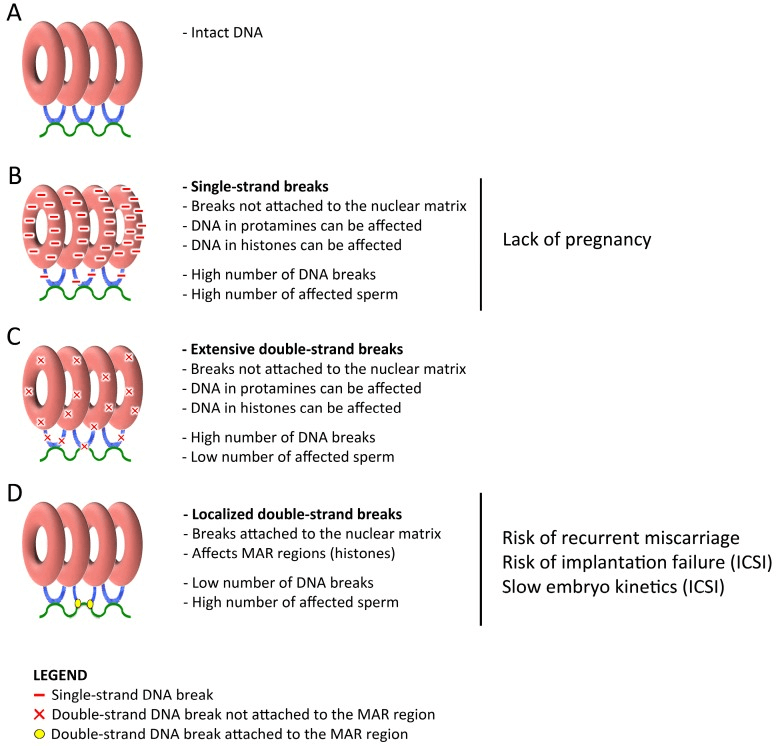
Typically, our DNA wraps around a protein called histones to form chromosomes. But to further compact the DNA into the sperm head, histones are exchanged for another protein called protamine, which can better compact the sperm genomes into donut-shaped structures. This process is called “protamination.” These donuts have regions that are linked to packing strings (nuclear matrix) inside the sperm head. 8
What causes sperm DNA fragmentation?
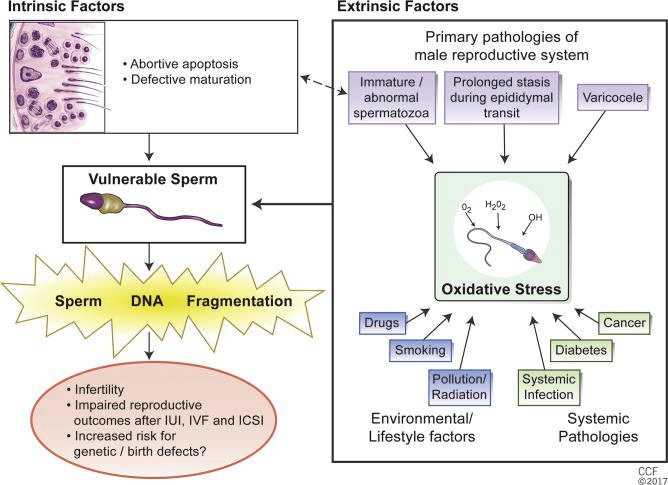
DNA damage can occur both during sperm production and transport. However, most of the DNA damage that contributes to sDF happens as the semen travels out of the testes into the semen tube (epididymis) prior to ejaculation.
Single strand breaks are caused by reactive oxygen species, such as environmental toxicants, smoking, alcohol, diet, radiation, infection, varicocele, or even the sperm’s own metabolism. 1112 Double-strand breaks are more likely caused by attempted cellular suicide (apoptosis) during the sperm production process or by enzymes triggered by heat and oxidative stress.
Factors that influence sperm DNA damage and are indications for testing sperm DNA fragmentation include: 131415
- Infection
- High fever and elevated testicular temperature
- Varicocele (enlargement of the veins in the scrotal sac)
- Advanced paternal age (>30)
- Obesity and Poor diet
- Drug use and Cigarette smoking
- Exposure to environmental and occupational pollutants
- Increased length of sexual abstinence
- Stress
- Alcohol abuse
Sperm and semen factors that may increase sDF include:
- Reduced antioxidants in semen and sperm cells
- Poor sperm DNA packaging, including due to protamine deficiency 16
What are sperm DNA fragmentation symptoms?
Most men are unaware that they have sDF until they try to have children because there are no symptoms. sDF contributes to male infertility, failed assisted reproduction technique (ART, including IVF) treatment cycles, or recurrent miscarriage. 17
High DNA fragmentation is associated with reduced sperm count, motility, and morphology. 1819 But it is totally possible to have sDF with normal semen analysis results, so you may need specific tests for sDF if you struggle with infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss. 20 Keep in mind, also, that they don’t routinely test for sDF as doctors disagree on its usefulness, so you may want to ask your doctor about it.
sDF destabilizes the embryonic genome, which can stop development and disturb implantation, leading to early miscarriages. 21 The paternal genome is switched on from day two of development and that is when sDF is more likely to affect embryonic development. 22 DNA damage in the embryo could also lead to cell degeneration and genetic mutations, causing congenital genetic diseases and childhood cancers. 232425
sDF is associated with the following negative pregnancy outcomes: 26
Sperm DNA fragmentation diagnosis
Semen analysis
Semen analysis (also called spermogram or seminogram) evaluates sperm appearance and semen composition, such as semen volume, pH, sperm concentration, motility, vitality, and morphology. 33 Subfertile men with abnormal sperm parameters do have more sDF than fertile men. 34 However, while defective genetic material is associated with abnormal sperm, this test does not directly test for genetic defects.
Almost 15% of infertile men have normal semenalysis, according to the WHO 2010. 35 Interestingly, these patients with normal sperm parameters can also have high sperm DNA fragmentation.
Specific sDF tests
sDF tests are controversial because some studies showed that sDF correlates with positive ICSI outcomes, but others show the opposite result. 3637 The conflicting results and lack of large clinical studies led the American Society for Reproductive Medicine to recommend against these tests. 38 In addition, there isn’t an established threshold for sDF test values or a standardized treatment protocol. 39 Therefore, many fertility specialists only check for sDF once they already rule out all the other causes, but some prefer to test it early on.
Indications for sDF tests include: 40
- Unexplained infertility
- Poor embryo development
- Multiple failed IVF/ICSI treatment
- Recurrent miscarriage
- Advanced age (>30 years)
- Varicocele
- Poor semen parameters (spermogram)
- Exposure to harmful substances
The most common tests include the Comet assay, the terminal transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay, Sperm Chromatin Structure Assay (SCSA), and the Sperm Chromatin Dispersion (SCD or Halo) test. 41 These tests are not created equal because each measures different types of DNA damage (See table). 4243
| Test | What it measures | Types of DNA damage detected | Caveats |
| TUNEL | The number of nicked and free DNA ends | Single-strand breaks Extensive double-strand breaks | Does not detect double-strand breaks in regions that attach to nuclear matrix |
| SCSA | Broken DNA is more likely to denature and take up red dye. Unbroken DNA emits green color. | Single strand breaks Extensive double strand breaks | Does not detect double-strand breaks in regions that attach to nuclear matrix. Is an indirect test. May measure more susceptibility to DNA damage than actual damage 44 |
| SCD | Fragment size of DNA denatured into single-strands with chemical or heat | Single-strand breaks Extensive double strand breaks | Does not detect double-strand breaks in regions that attach to nuclear matrix |
| Neutral Comet | Amount of double-stranded fragmented DNA | All double strand breaks, including in regions that attach to nuclear matrix | |
| Alkaline Comet | Amount of double and single strand fragmented DNA | All double and single strand breaks | |
| Two-tailed Comet | Combination of neutral and alkaline Comet | Single-strand breaks Extensive double strand breaks | Less standardized test |
| Toluidine blue staining | Overall DNA integrity inside sperm heads | Fast but non-DFI test | |
| CMA3 staning | Sperm DNA protamination | Non-DFI test, value >30% lowers ICSI fertilization rate 45 |
TUNEL, SCSA, and SCD results typically correlate with alkaline Comet but not neutral Comet results. This is because only the neutral Comet can detect localized strand breaks between the donut structures that attach to the nuclear matrix. 46
Reference ranges
These tests measure DNA damage and display results as DNA Fragmentation Index (DFI), which shows the percentage of cells with seriously damaged DNA. 47
For instance, reference levels in SCSA are following: 48
- ≤ 15% DFI = excellent to good sperm DNA integrity
- > 15 to < 25% DFI = good to fair sperm DNA integrity
- > 25 to < 50% DFI = fair to poor sperm DNA integrity
- ≥ 50% DFI = very poor sperm DNA integrity
With the TUNEL technique, studies have shown that DFI >20% indicates poor sperm DNA quality, and can be used to distinguish between fertile and infertile men. 49
Treatments for Sperm DNA fragmentation
Lifestyle Changes
sDF has a major lifestyle contributor, so treating sDF involves diet and lifestyle changes to reduce oxidative stress and DNA damage in sperm cells, including: 5051
- Fever reduction with antipyretics (paracetamol, ibuprofen)
- Treating the infections
- Quit drugs, smoking and occupational hazards (vibrations, Heavy metals, PVC)
- Diet – fresh foods, particularly those containing antioxidants and vitamin C & E
- Avoiding toxic exposures
- Varicocele surgery
- Frequent ejaculation
| Lifestyle risk factors | Lifestyle modifications |
| Smoking (Nicotine, Cd, Pb, Benzo(a)-pyrene)- Oxidative stress causes significant DNA fragmentations and spermatozoids are especially susceptible to it 52 | Cessation of smoking |
| Air pollution (Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and air particulate matter) can damage DNA 53 | Avoid spending time outside in high pollution hours, wear face masks, and spend more time in nature. |
| POP: organochlorine pesticides, such as DDT, industrial chemicals, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB), unintentional by-products of many industrial processes, such as polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDD) and dibenzofurans (PCDF) or ‘dioxins’ 54 | PCB accumulates in the ends of the food chain: Avoid fatty fish, especially farmed. |
| Infection – Overall inflammation causes oxidative stress leading to damage DNA in spermatozoa 55 | Antibiotics and antipyretics (this includes something so seemingly irrelevant such as bad teeth) |
| Testicular heat – Increase in DNA fragmentation with 2–3°C temperature increase 56 | Avoid cycling with tight pants, sauna use, using laptops on closed legs |
| Mobile phone radiation – increased levels of SDF and decreased antioxidants [39,40] 5758 | Do not store mobile phone in trouser pocket and/or consider radiation-blocking underwear |
| UV radiation – Sperm genetic material is at higher risk of DNA fragmentation due to UV radiation (254 nm) 59 | Avoid professional hazards |
| Caffeine – Some authors believe it might cause higher SDF, especially in unprotaminated regions, but there is no consensus 60 | Reduce coffee intake |
| Alcohol – Alcohol may increase the percentage of spermatozoa with DNA fragmentation and apoptosis 61 | Reduce alcohol intake to one unit maximum per day, preferably as red wine, because it contains antioxidants |
| Drugs – Ecstasy and opiates create oxidative stress metabolites 62 | Cessation of drug intake |
| Heavy metals – Increase in percentage of spermatozoa with DNA fragmentation 63 | Avoid occupational exposure and smoking or exposure to cigarette smoke. Avoid fish with high mercury levels. |
| Bisphenol A and PVC – Linked with semen quality, DNA integrity, oxidative stress in infertile men 64 | Avoid plastic packaging, canned foods. Don’t heat or store food in plastic containers. |
| Obesity – Poor spermatogenesis and associated with high SDF 65 | Losing weight through healthy diet and exercise |
| Imbalanced diet – Lack of antioxidants needed to repair DNA damage 66 | Better diet. Include more foods rich in vitamins E and C such as fruits and vegetables, e.g. pepper, cabbage, fish, and nuts. Oxidant supplements such as vitamins E and C, selenium, coenzyme Q10, N-acetylcysteine, zinc, and L-carnitine |
| Abstinence – Supposedly leads to accumulation of spermatozoids with DNA that hasn’t been repairing DNA 67 | Frequent ejaculation, more than once a day 68 |
After three months of these initiatives to reduce sDF, it is a good idea to retest for sDF levels to see if the changes are working. 69
Fertility Treatments
sDF testing may have very important predictive value for fertility treatments. Couples with low sperm DNA damage can succeed with traditional intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF). Whereas, when DFI values are higher, directly injecting sperms into the cytoplasm of eggs (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection, ICSI) instead of traditional IVF may increase the chance of success. 7071 Traditional IVF exposes the egg to the sperms in the test tube for 90 minutes, whereas ICSI directly injects the sperm into the oocyte. Therefore, ICSI might reduce the amount of time both the eggs and sperms are exposed to reactive oxygen species. 72 ICSI typically costs more than IVF, and may also confer some health risks in the offspring, 73 so ICSI is usually considered only after IVF is unsuccessful.
Typically, natural ejaculates are noninvasively collected and used for IVF and ICSI. In men with sDF, most of the sperm DNA damage that contribute to infertility and miscarriage happens once the semen leaves the testicle for an ejaculation. 74 Therefore, direct aspiration of sperm from the testicle (testicular sperm aspiration, TESA) may improve the chance of a successful pregnancy than ejaculate for these men. 75 However, TESA is not without risk—it is an invasive surgical procedure with small chances of complications, including infection, bleeding, and testicular atrophy. 76 In addition, TESA combined with ICSI may increase the chance of chromosomal abnormalities in the embryo and offspring. 77
Can you have a successful pregnancy with sDF?
Fortunately, couples where the male partner has a high percentage of sperm DNA fragmentation have had successful pregnancies. Your chances will be higher if the percentage of sperm bearing high levels of SDF is lower. The chances of successful pregnancies are also greater if the spermatozoids with high DNA fragmentation fertilize younger oocytes, which are much more efficient at repairing sperm DNA damages. 78
Next Steps to Consider
- Ask your doctor about testing for sDF
- If you do find this is an issue, look into solutions for decreasing fragmentation
- One simple strategy for decreasing fragmentation is to have your partner ejaculate prior to trying to conceive
References




0 Comments